Functions of the Urinary System:
- Excretion
- Regulation of blood volume and pressure
- Regulation of the concentration of solutes in the blood
- Regulation of extracellular fluid pH
- Regulation of red blood cell synthesis
- Regulation of vitamin D synthesis
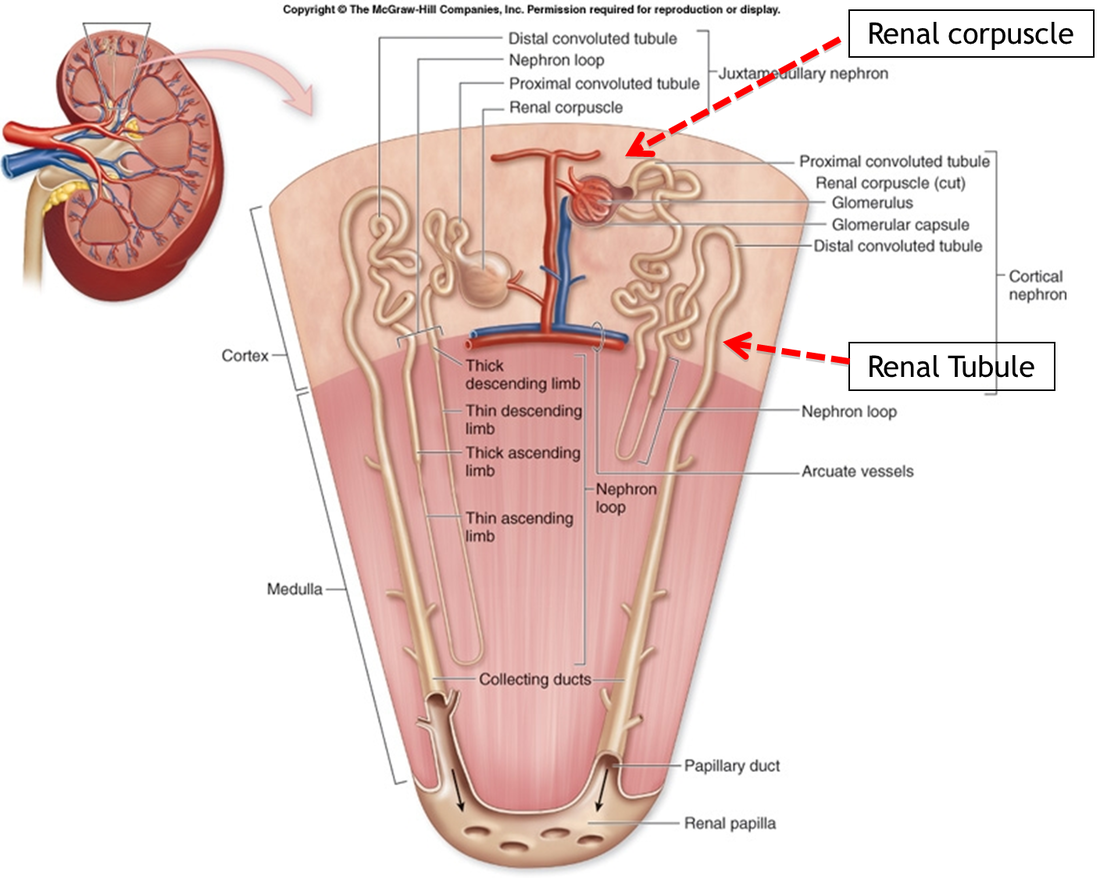
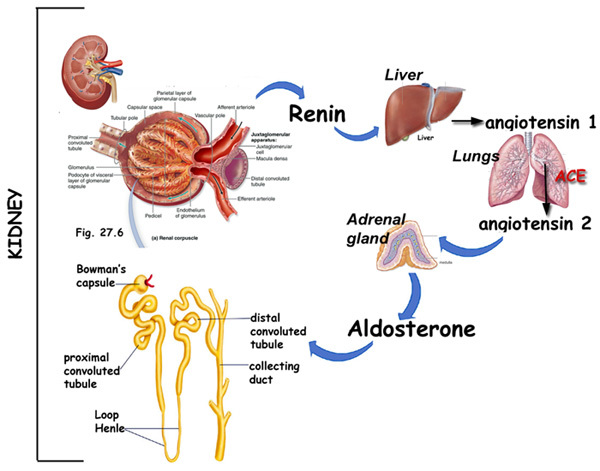
The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron and there are approximately 1.3 million of them in each kidney. Each nephron consists of a renal corpuscle, a proximal convoluted tubule, a loop of hence, and a distal convoluted tubule.
Urine Formation:
Urine Formation:
- Filtration. Filtration is the movement of materials across the filtration membrane into Bowman's capsule to form filtrate.
- Tubular Reabsorption. Solutes are reabsorbed across the wall of the nephron into the interstitial fluid by transport processes, such as active transport and cotransport. Water is reabsorbed across the wall of the nephron by osmosis. Water and solutes pass from the interstitial fluid into the peritubular capillaries.
- Tubular secretion. Solutes are secreted across the wall of the nephron into the filtrate.
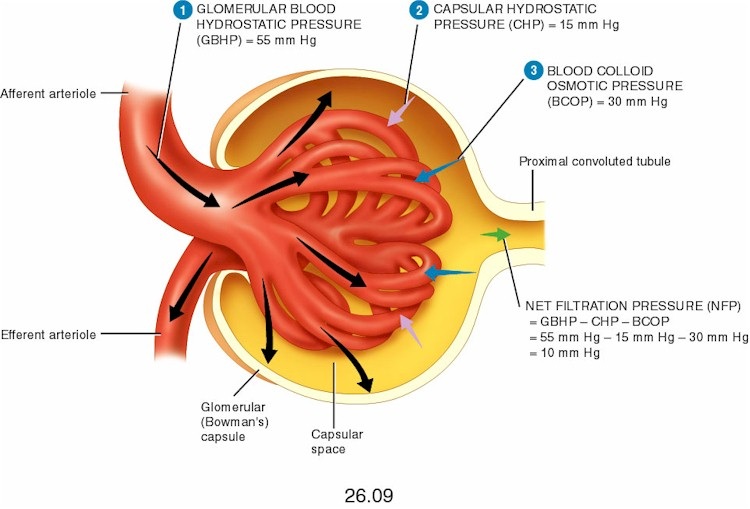
Filtration Pressure:
- Glomerular capillary pressure, the blood pressure within the glomerulus, moves fluid from the blood into Bowman's capsule.
- Capsular pressure, the pressure inside Bowman's cap sure, moves fluid from the capsule into the blood.
- Colloid osmotic pressure, produced by the concentration of blood proteins, moves fluid from Bowman's capsule into the blood by osmosis.
- Filtration pressure is equal to the glomerular capillary pressure minus the capsular and colloid osmotic pressures.
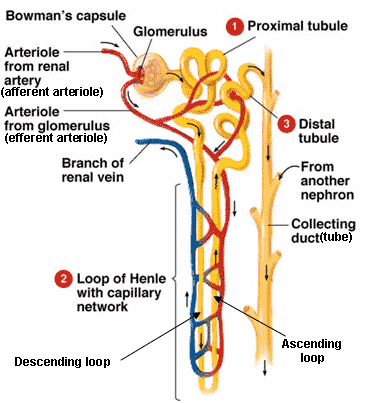
Reabsorption in the Loop of Henle:
- The wall of the thin segment of the descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to water and, to a lesser extent, to solutes. The interstitial fluid in the medulla of the kidney and the blood in the vasa recta have a high solute concentration. Water therefore moves by osmosis from the tubule into the interstitial fluid and into the vasa recta. An additional 15% of the filtrate volume is reabsorbed. To a lesser extent, solutes diffuse from the vasa recta and interstitial fluid into the tubule.
- The thin segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is not permeable to water but is permeable to solutes. The solutes diffuse out of the tubule and into the more dilute interstitial fluid as the ascending limb projects toward the cortex. The solutes diffuse into the descending vasa recta.
Renin and angiotensin help regulate aldosterone secretion. Renin, an enzyme secreted by cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatuses in the kidneys. Renin acts on angiotensinogen, a plasma protein produced by the liver, and converts it to angiotensin I. Angiotensin I is rapidly converted to a smaller peptide called angiotensin II by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II acts on the adrenal cortex, causing it to secrete aldoesterone.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed