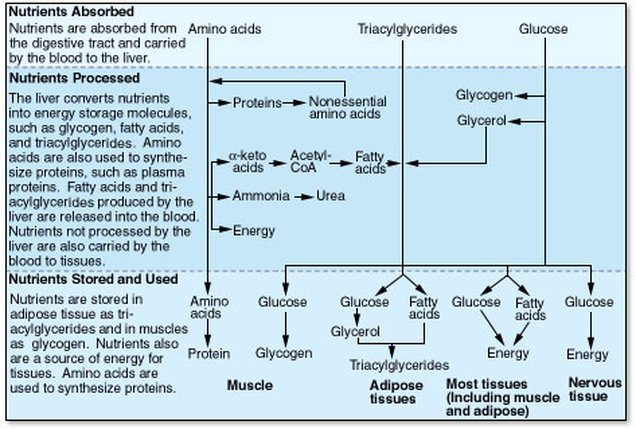
- Nutrients are the chemicals taken into the body that provide energy and building blocks for new molecules.
- Essential nutrients are nutrients that must be ingested because the body cannot manufacture them- or it cannot manufacture them in adequate amounts.
- Carbohydrates include monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Although most of the carbohydrates we ingest are derived from plants, lactose is derived from animals. The most common monosaccharides in the diet are glucose and fructose. Plants capture energy from sunlight and use that energy to produce glucose, which can be found in vegetables, fruits, molasses, honey, and syrup. Fructose is most often derived from fruits and berries.
- Complex carbohydrates are large polysaccharides, which are composed of long chains of glucose. Examples are starch, glycogen, and cellulose, which differ from one another in the arrangement of the glucose molecules and the structure of the chemical bonds holding them together. Starch is an energy-storage molecule in plants and is found primarily in vegetables, fruits, and grains. Glycogen is an energy-storage molecule in animals and is located primarily in muscle and in the liver. cellulose forms plant cell walls.
- Lipids include triglycerides, steroids, phospholipids, and fat-soluble vitamins. Trigylcerides, are the most common type of lipid in the diet, accounting for about 95% of the total lipid intake.
- Proteins are chains of amino acids. They are found in most of the plant and animal products we eat. Proteins in the body are constructed of 20 different kinds of amino acids, which are divided into two groups: essential amino acids and nonessential amino acids. Essential amino acids are those the body cannot synthesize, so they must be obtained in the diet. The nine essential amino acids are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, and valine. Nonessential amino acids are necessary to contract our proteins but do not necessarily need to be ingested, since they can by synthesized from the essential amino acids.
- Vitamins are organic molecules that exist in minute quantities in food and are essential to normal metabolism. Essential vitamins cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet.
- Minerals are inorganic nutrients that are essential for normal metabolic functions. people ingest minerals alone or in combination with organic molecules.
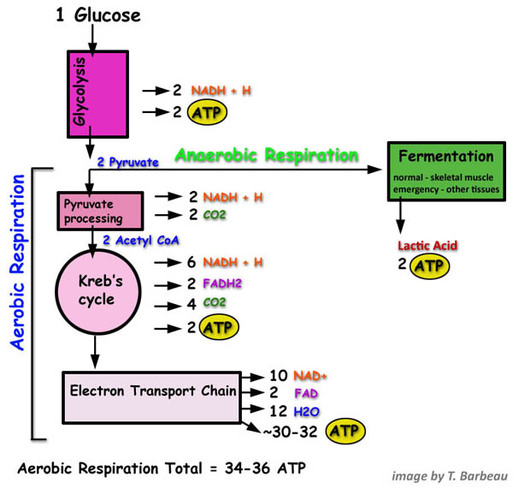
Aerobic Respiration:
- Glycolysis in the cytoplasm converts glucose to two pyretic acid molecules and produces two ATP and two NADH. The NADH can go to the electron-transport chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- The two pyruvic acid molecules produced in glycolysis are converted to two acetyl-CoA molecules, producing two CO2 and two NADH can go to the electron-transport chain.
- The two acetyl-CoA molecules enter the citric acid cycle, which produces four Co2, six NADH, two FDH, and two ATP. The NADH and FADH2 can go to the electron-transport chain.
- The electron-transport chain uses NADH and FADH2 to produce 34 ATP. This process requires O2, which combines with H+ to form H2O.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed